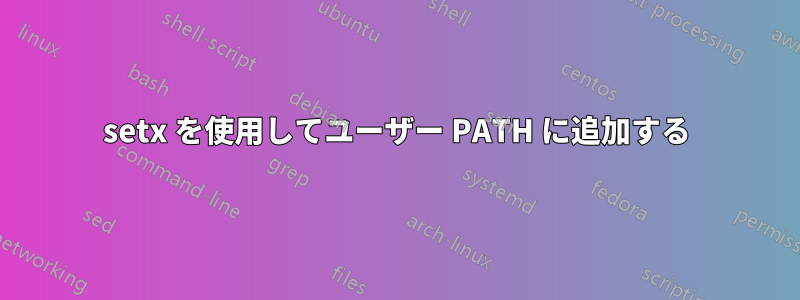
私の試み:
setx PATH "%PATH%;%~dp0"
システム PATH 内のすべてがユーザー PATH に重複しないようにするにはどうすればよいでしょうか?
答え1
システム PATH がユーザー PATH に重複しないようにするにはどうすればよいでしょうか?
オプションを使用します/m。
setx /m PATH "%PATH%;%~dp0"
ノート:
/m- システム環境 HKLM に変数を設定します。(デフォルトはローカル環境 HKCU です)
setx使用法
F:\test>setx /?
SetX has three ways of working:
Syntax 1:
SETX [/S system [/U [domain\]user [/P [password]]]] var value [/M]
Syntax 2:
SETX [/S system [/U [domain\]user [/P [password]]]] var /K regpath [/M]
Syntax 3:
SETX [/S system [/U [domain\]user [/P [password]]]]
/F file {var {/A x,y | /R x,y string}[/M] | /X} [/D delimiters]
Description:
Creates or modifies environment variables in the user or system
environment. Can set variables based on arguments, regkeys or
file input.
Parameter List:
/S system Specifies the remote system to connect to.
/U [domain\]user Specifies the user context under which
the command should execute.
/P [password] Specifies the password for the given
user context. Prompts for input if omitted.
var Specifies the environment variable to set.
value Specifies a value to be assigned to the
environment variable.
/K regpath Specifies that the variable is set based
on information from a registry key.
Path should be specified in the format of
hive\key\...\value. For example,
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\
Control\TimeZoneInformation\StandardName.
/F file Specifies the filename of the text file
to use.
/A x,y Specifies absolute file coordinates
(line X, item Y) as parameters to search
within the file.
/R x,y string Specifies relative file coordinates with
respect to "string" as the search parameters.
/M Specifies that the variable should be set in
the system wide (HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE)
environment. The default is to set the
variable under the HKEY_CURRENT_USER
environment.
/X Displays file contents with x,y coordinates.
/D delimiters Specifies additional delimiters such as ","
or "\". The built-in delimiters are space,
tab, carriage return, and linefeed. Any
ASCII character can be used as an additional
delimiter. The maximum number of delimiters,
including the built-in delimiters, is 15.
/? Displays this help message.
NOTE: 1) SETX writes variables to the master environment in the registry.
2) On a local system, variables created or modified by this tool
will be available in future command windows but not in the
current CMD.exe command window.
3) On a remote system, variables created or modified by this tool
will be available at the next logon session.
4) The valid Registry Key data types are REG_DWORD, REG_EXPAND_SZ,
REG_SZ, REG_MULTI_SZ.
5) Supported hives: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE (HKLM),
HKEY_CURRENT_USER (HKCU).
6) Delimiters are case sensitive.
7) REG_DWORD values are extracted from the registry in decimal
format.
参考文献
- Windows CMD コマンドラインの AZ インデックス- Windows コマンド ラインに関連するあらゆることに関する優れたリファレンス。
- セットx- 環境変数を永続的に設定します。SETX を使用して、マシン (HKLM) または現在ログオンしているユーザー (HKCU) の環境変数を設定できます。
答え2
[CMD、WMIC、HKLM、HKCU、SETX、PATH、2001]
この問題はおそらく20年以上前から存在している。
-setx パス "%Path%;NewPath"ユーザー パスがシステム パスで汚染されます。
-setx パス "%Path%;NewPath" /Mシステム パスをユーザー パスで汚染します。
-汚染:ビデオ
コマンド プロンプトを排他的に使用する非 ANSI ディレクトリを考慮した安全なネイティブ ソリューションがあるかどうかはわかりません。
これは私の試みです!
- Microsoft Windows [バージョン 10.0.19042.868] を使用
0- パスを確認する
echo %Path%
reg query "HKCU\Environment" /v Path
reg query "HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Environment" /v Path
reg EXPORT "HKCU\Environment" UserEnvironment.reg /y
reg EXPORT "HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Environment" SystemEnvironment.reg /y
wmic ENVIRONMENT where "username='<SYSTEM>' AND name='Path'" get variablevalue
wmic ENVIRONMENT where "username='%COMPUTERNAME%\\%USERNAME%' AND name='Path'" get variablevalue
ヒント: wmic ENVIRONMENT get *[続きを見る]
情報: 上記のコマンドを使用してレジストリのバックアップが実行されました。ファイルは現在のディレクトリに保存されました。
1- バックアップユーザーパス%USERPATH%
- コマンドの前提条件:
- NULL以外のパス。
- 機能パス;
- もしヌルまたは機能しないパスのみ行うステップ "2「
wmic ENVIRONMENT where "username='%COMPUTERNAME%\\%USERNAME%' AND name='Path'" get variablevalue | more +1 > %temp%\userpathvalue.txt
情報: 文字列の末尾に若干の汚染*があります。
set /P USERPATH=<%temp%\userpathvalue.txt
-'/'スペースを見やすくするために追加します
set "USERPATH=%USERPATH%/"
- 最大15個の末尾のスペースを削除し、その後「/」を削除します。
set "USERPATH=%USERPATH: /=/%"
set "USERPATH=%USERPATH: /=/%"
set "USERPATH=%USERPATH: /=/%"
set "USERPATH=%USERPATH: /=/%"
set "USERPATH=%USERPATH:/=%"
情報: 導入されたスペースの数は私のテストでは一貫していませんでした。
echo %USERPATH%[checking final string]
setx USERPATH "%USERPATH%"
* 非表示の文字を扱う場合は、16 進数に変換すると識別しやすくなります。次のようにします。
wmic ENVIRONMENT where "username='%COMPUTERNAME%\\%USERNAME%' AND name='Path'" get variablevalue | more +1 > %tmp%\0 && set /P TEMPREADER=<%tmp%\0
echo %TEMPREADER% >%tmp%\1 && echo %TEMPREADER%/ && certutil -f -encodehex "%tmp%\1" "%tmp%\2" 11 | more +4 && type "%tmp%\2"
REM to open on notepad, type: certutil -f -encodehex "%tmp%\1" "%tmp%\2" 5 && cmd /C START "" /MAX notepad %tmp%\2
ヒント: encodehex で 4、5、10、11 (none と同じ) を使用します
2- ユーザーパスを%USERPATH%次のように設定します。
setx PATH ^%USERPATH^%
終わり!
¹情報:setx PATH "%USERPATH%"変数を設定する価値代わりにリテラル %USERPATH%;
²情報: リテラルを使用する方が、動作が静的ではなく動的になるため優れています。つまり、値の代わりにリテラルを使用すると、%USERPATH%将来的には変数のみを変更する必要があります。一方、値 (つまり、変数内に存在するアドレス) を使用すると、%PATH%変更時にユーザー変数も更新する必要があります%USERPATH%(これは望ましくありません)。
³情報: 以下の方法は推奨されません。機能しますが、間違いを起こしやすくなります。
reg add "HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Environment" /v PATH /d ^%USERPATH^% /f
wmic ENVIRONMENT set name="PATH", variablevalue=^%USERPATH^%, username="%COMPUTERNAME%\\%USERNAME%"
3- 今のところは%USERPATH%
setx USERPATH "%USERPATH%;ENTER-NEW-PATH-HERE"
ヒント: 続行する前に、すべてのプログラム、特にターミナルを閉じてください。
4- 再確認
echo %Path%
reg query "HKCU\Environment" /v Path
reg query "HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Environment" /v Path
wmic ENVIRONMENT where "username='<SYSTEM>' AND name='path'" get variablevalue
wmic ENVIRONMENT where "username='%COMPUTERNAME%\\%USERNAME%' AND name='path'" get variablevalue
5- 目視検査
rundll32 sysdm.cpl,EditEnvironmentVariables
情報: システム PATH は、前のコマンドが管理者権限で起動された場合にのみ変更できます。
6-要約:やれ!/or don't!
REM the commands pre-suppose
REM - non-null path;
REM - functional path;
REM if null or unfunctionl path don't progress!
reg query "HKCU\Environment" /v Path
reg query "HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Environment" /v Path
reg EXPORT "HKCU\Environment" UserEnvironment.reg /y
reg EXPORT "HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Environment" SystemEnvironment.reg /y
wmic ENVIRONMENT where "username='%COMPUTERNAME%\\%USERNAME%' AND name='Path'" get variablevalue | more +1 > %temp%\userpathvalue.txt
set /P USERPATH=<%temp%\userpathvalue.txt
set "USERPATH=%USERPATH%/"
set "USERPATH=%USERPATH: /=/%"
set "USERPATH=%USERPATH: /=/%"
set "USERPATH=%USERPATH: /=/%"
set "USERPATH=%USERPATH: /=/%"
set "USERPATH=%USERPATH:/=%"
echo %USERPATH%[checking final string] && echo %USERPATH% > %tmp%\0
certutil -f -encodehex "%tmp%\0" "%tmp%\1" 11 | more +4 && type "%tmp%\1"
setx USERPATH "%USERPATH%"
setx PATH ^%USERPATH^%
echo done!
REM setx USERPATH "%USERPATH%;ENTER-NEW-PATH-HERE"
REM please close all programs
乾杯!
答え3
あなたがやろうとしていることについては、このページで説明されているようです: SETX や PATHMAN などで PATH を追加しますか? あるいは、質問に詳細を追加して、これがどのように異なるのかを理解できるようにしてください。ただし、そのページには、質問されている問題と同じか類似の問題に対する複数の解決策があります。


